i.Mune® NEO [CE]
(not available in the United States of America)

CD3+ T-Lymphocyte Quantification in Dried Blood Spots (DBS)
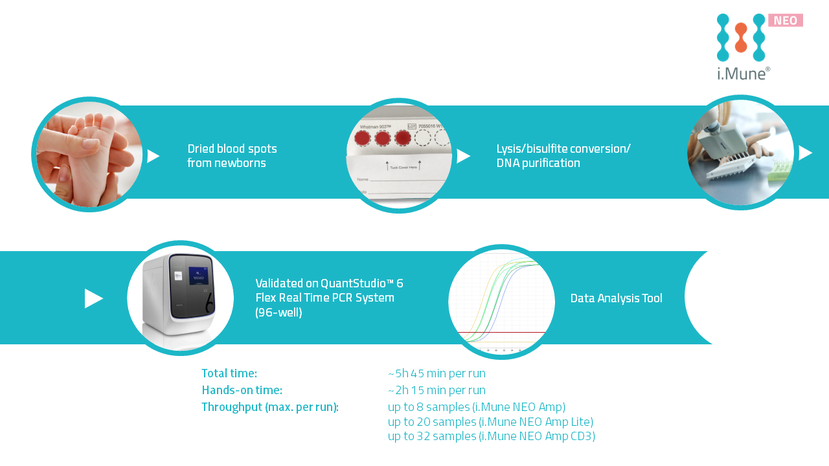
i.Mune NEO is a quantitative in vitro diagnostic test to determine the percentages of T-lymphocyte (CD3+) in newborn capillary whole blood specimens collected and dried on filter paper.
The test uses a real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with fluorescent hydrolysis probes for the detection of the immune cell type specific demethylated genomic target regions.
The determination of the percentage of T lymphocytes with i.Mune NEO can be used as a second-tier test for samples with conspicuous TREC screening results to identify newborns at risk of suffering from Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID).
Quantification of Additional Immune Cell Types
In addition to T-lymphocytes, i.Mune NEO can be used to determine other immune cell types using the same technology to further characterise samples with abnormal TREC screening results, as SCID patients present with different immunophenotypes (Tangye et al., 2022). This application has not been clinically validated using i.Mune NEO.
- T-lymphocytes (CD3+)
- Memory Helper T lymphocytes (CD3+CD4+CD45RO+)
- B lymphocytes (CD19+)
- Natural Killer lymphocytes (CD16+CD56dim)
- Helper T lymphocytes (CD3+CD4+)
- Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CD3+CD8+)
The i.Mune NEO [CE] test consists of the following kits:
Test Procedure
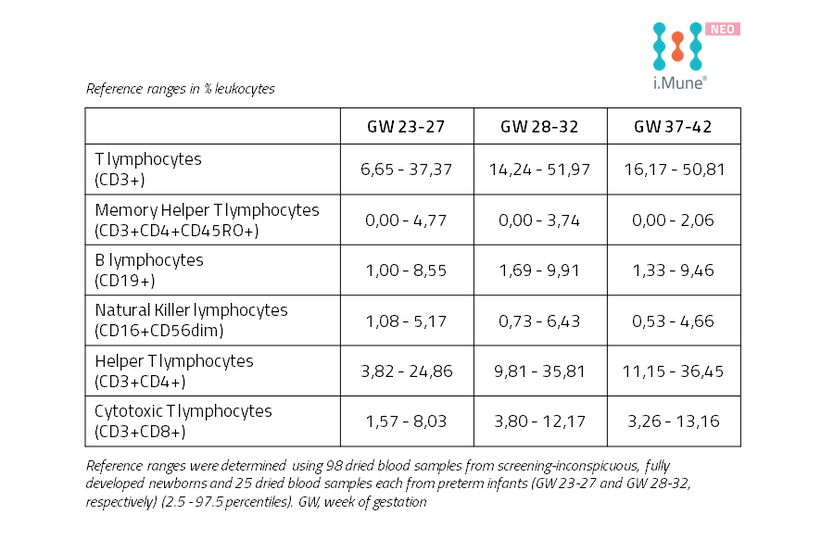
Reference Ranges
Literature
Epigenetic quantification of CD3+ T lymphocytes for second-tier testing after conspicuous SCID (Severe Combined Immunodeficiency) screening findings (Blom et al., 2021)1)
Second tier testing using epigenetic immune cell quantification can reduce the number of non-actionable secondary findings and false-positive referrals in newborn screening for SCID.
Potential Applications:
- Second-tier testing after conspicuous TREC newborn screening findings
References
- Blom, M et al. Second Tier Testing to Reduce the Number of Non-actionable Secondary Findings and False-Positive Referrals in Newborn Screening for Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021).
- Baron U et al., Epigenetic immune cell counting in human blood samples for immunodiagnostics. Sci Transl Med. 2018 Aug 1;10 (452)